BIS CERTIFICATION FOR QUENCHED AND TEMPERED ALLOY STEEL FORGINGS
IS 12145:1987
In this competitive scenario, it isn't easy to survive in the market without a standard quality and certified product. BIS license may also be required to sell products in the Indian market.
To get BIS certification and produce a standard quality product, the manufacturer must ensure that their product must follow the specified Indian standard.
Let's take a closer look at IS 12145:1987 for quenched and tempered alloy steel forgings for pressure vessels.
This standard specifies the requirements for quenched and tempered alloy steel forgings for pressure vessels, such as those used in the reactor system. Forgings for vessel closures, flanges, shells, tube sheets, heads, rings, and similar parts are specifically covered in this standard.
According to IS 12145: 1987, forgings are classified into 3 grades: I, II and III based upon chemical composition (C, Mn and Alloy Content (Ni, Cr, Mo)) and Mechanical Properties (YS, TS, Elongation, Impact).
Grades I and II have been subdivided into I A, I B, and II A, II B, with higher YS for B grades. Grade III has the lowest carbon content, the highest alloy content, and the highest YS among the 3 grades.
The general requirements for material supply shall be as specified in the standard. The forgings must be made from killed steel produced by any of the primary processes, such as open hearth, basic oxygen, or electric furnace, and may be followed by secondary steel production processes.
To ensure adequate deformation throughout the sections, forgings must be mechanically hot worked using a suitable process. After hot working, the forgings must be cooled to achieve complete austenite transformation without any detrimental effects such as cracking or distortion.
All forgings shall be heat-treated, which includes quenching and tempering. Following tempering, the forgings must be slowly cooled from the tempering temperature. The finished forgings must be subjected to product analysis. The mechanical properties of the forgings shall be as specified in the standard.
TESTS
Tests shall be carried out in accordance with the method prescribed in the standard.
- Chemical composition analysis
- Mechanical tests
- Appearance
- Shapes, dimensions and tolerances
- Ultrasonic testing
Marking:
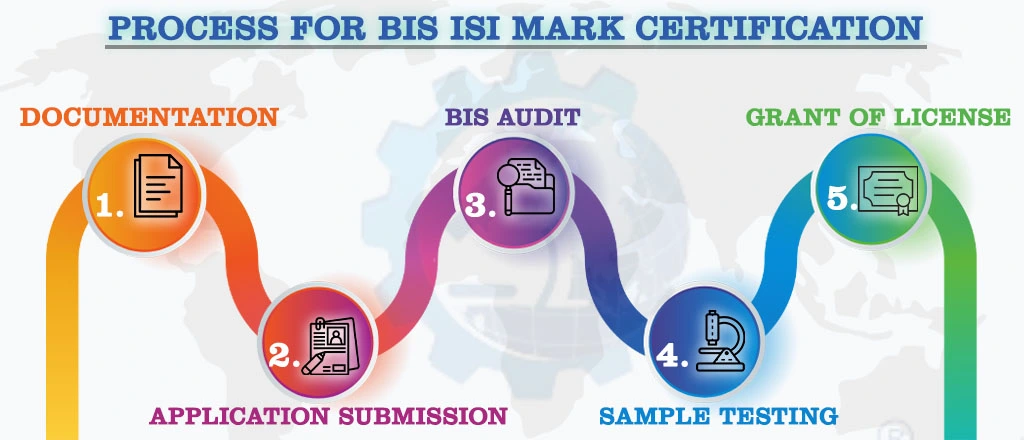
Each forging must be stamped with the grade of material, heat number or identification mark, and the manufacturer's trademark. The standard mark (ISI Mark) may also be applied to the forgings. The Manufacturer must obtain a BIS license from the Bureau of Indian Standards to use a standard mark (ISI Mark). The Bureau grants a license based on a successful assessment of manufacturing infrastructure, production process, and quality control and testing capabilities during a visit to its manufacturing premises.
NOTE:
For Detailed Information about the Procedure for BIS ISI Certification
Visit :
• ISI Mark Certification for Domestic Manufacturers• ISI Mark Certification for Foreign Manufacturers
Conclusion:
If a product falls under the scope of the BIS Conformity Assessment Scheme, All the manufacturers, importers, and foreign entities must obtain BIS ISI Certification. The Bureau may cancel the License if the product fails to meet certification requirements.
Aleph INDIA has been serving the industry as a single-window operator for all product regulatory compliance. We can assist importers or manufacturers in meeting all criteria for importing or selling a product in the Indian market.
International Audits & Participation
Testimonials
BIS REGISTRATION FOR ELECTRONIC & IT PRODUCT
In the era of globalization, world trade is growing rapidly and henceforth, Manufacturing and Import/Export businesses are also growing drastically...View More
BIS CERTIFICATE FOR FOREIGN MANUFACTURER
The Economy of India-the fastest developing economy on the globe with the capabilities that help it matches up with the biggest international...View More
PRODUCT CERTIFICATION SCHEME (ISI MARK) FOR DOMESTIC MANUFACTURERS
Anything a person buys from food to cars, clothes to electronics, branded to unnamed products there is always a question that wanders in one’s...View More
WIRELESS PLANNING AND COORDINATION (WPC)
WPC: Wireless means communication done from one point to another point without the wires and cables. Electromagnetic waves carry the ...View More
BUREAU OF ENERGY EFFICIENCY (BEE) CERTIFICATE
BEE CERTIFICATE: Energy is the future, and its conservation is the way of the bright future. Everyone claims the environment is important...View More
E-WASTE MANAGEMENT
E-waste is one of the world's fastest-growing trash streams. We currently manufacture almost 50 million tones of it each year...View More
Request a call back.
Would you like to speak to one of our Senior Technical advisers over the phone? Just submit your details and we’ll be in touch shortly. You can also email us if you would prefer.
BIS REGISTRATION FOR ELECTRONIC & IT PRODUCT
In the era of globalization, world trade is growing rapidly and henceforth, Manufacturing and Import/Export businesses are also growing drastically...View More
BIS CERTIFICATE FOR FOREIGN MANUFACTURER
The Economy of India-the fastest developing economy on the globe with the capabilities that help it matches up with the biggest international...View More
PRODUCT CERTIFICATION SCHEME (ISI MARK) FOR DOMESTIC MANUFACTURERS
Anything a person buys from food to cars, clothes to electronics, branded to unnamed products there is always a question that wanders in one’s...View More
WIRELESS PLANNING AND COORDINATION (WPC)
WPC: Wireless means communication done from one point to another point without the wires and cables. Electromagnetic waves carry the ...View More
BUREAU OF ENERGY EFFICIENCY (BEE) CERTIFICATE
BEE CERTIFICATE: Energy is the future, and its conservation is the way of the bright future. Everyone claims the environment is important...View More
E-WASTE MANAGEMENT
E-waste is one of the world's fastest-growing trash streams. We currently manufacture almost 50 million tones of it each year...View More
View All Services
Request a call back.
Would you like to speak to one of our Senior Technical advisers over the phone? Just submit your details and we’ll be in touch shortly. You can also email us if you would prefer.